Mobile Robotics Project
Integration of vision, navigation, and filtering for autonomous Thymio robot navigation.
This project, undertaken during the 2023 fall semester at EPFL for the “Basics of Mobile Robotics” course, focuses on integrating vision, global and local navigation, and filtering techniques to autonomously maneuver a Thymio robot within a predefined environment.
For a detailed walkthrough and access to the codebase, please visit the GitHub project repository.
This is a group project, see the GitHub Repository for more details about the group members.
Demonstration
A comprehensive demonstration showcasing all components of the project is available:
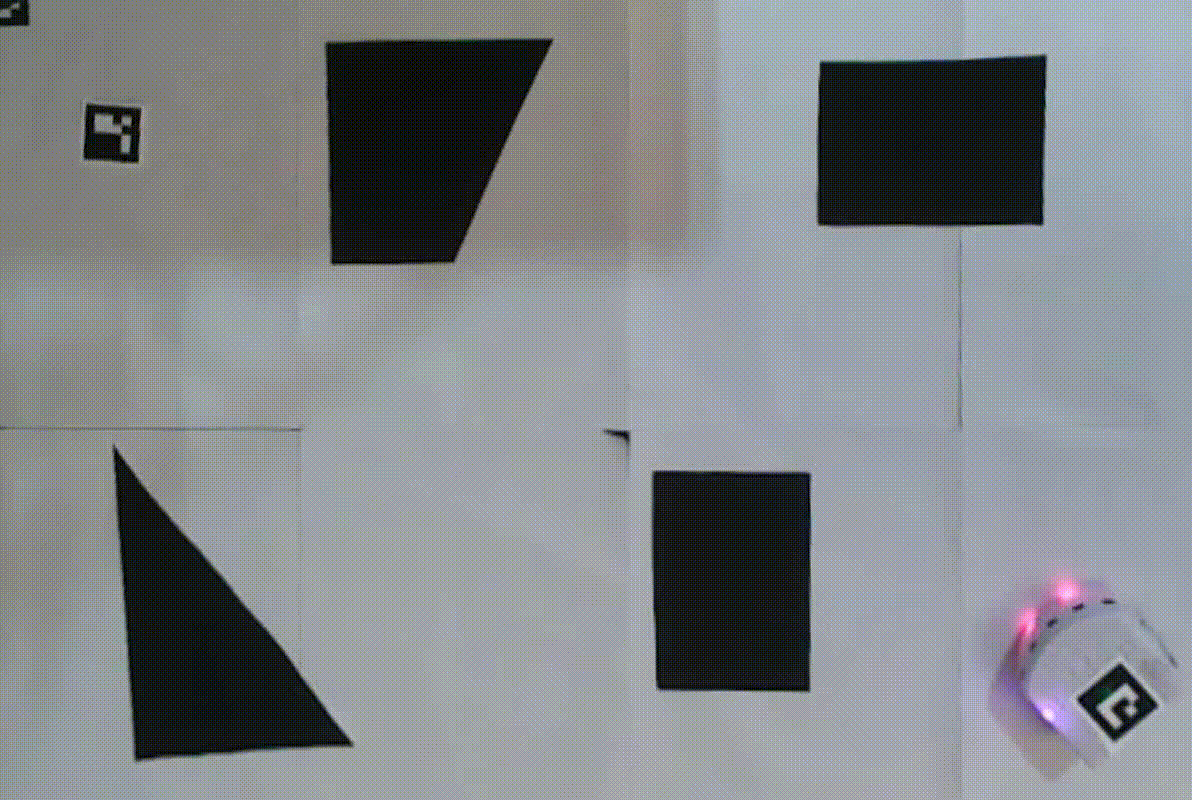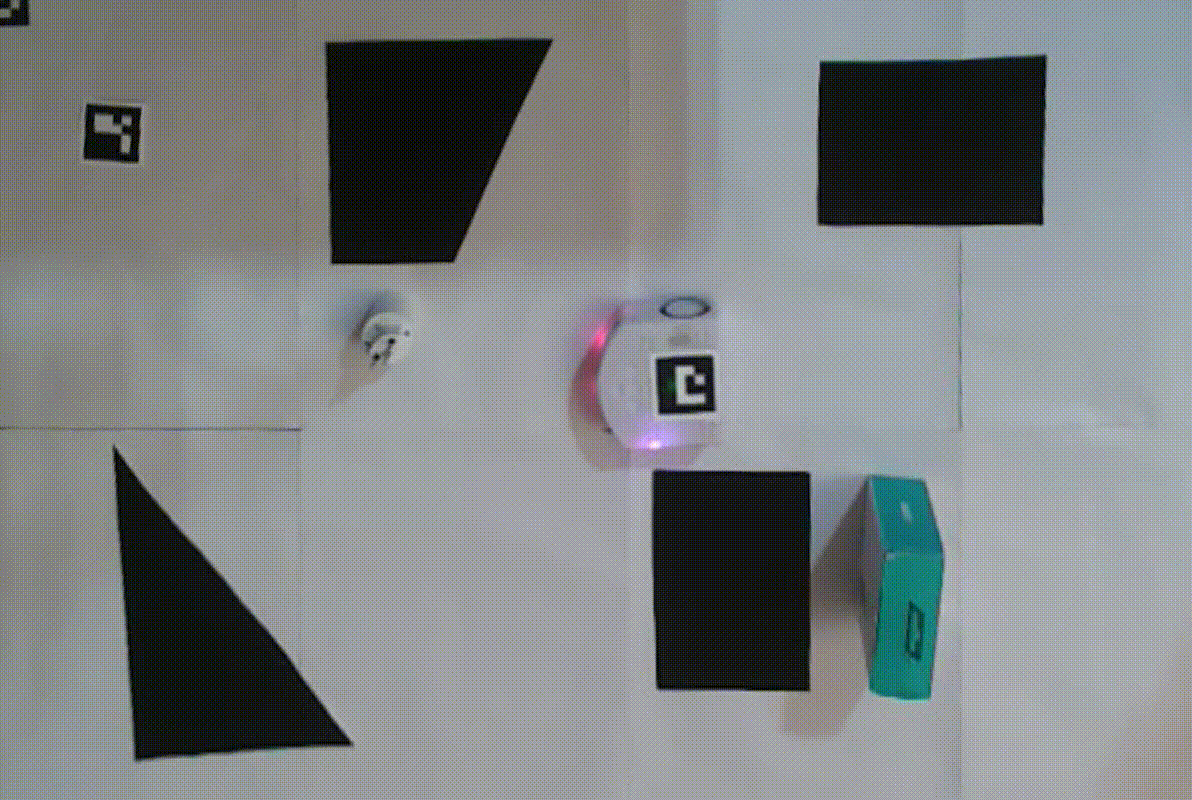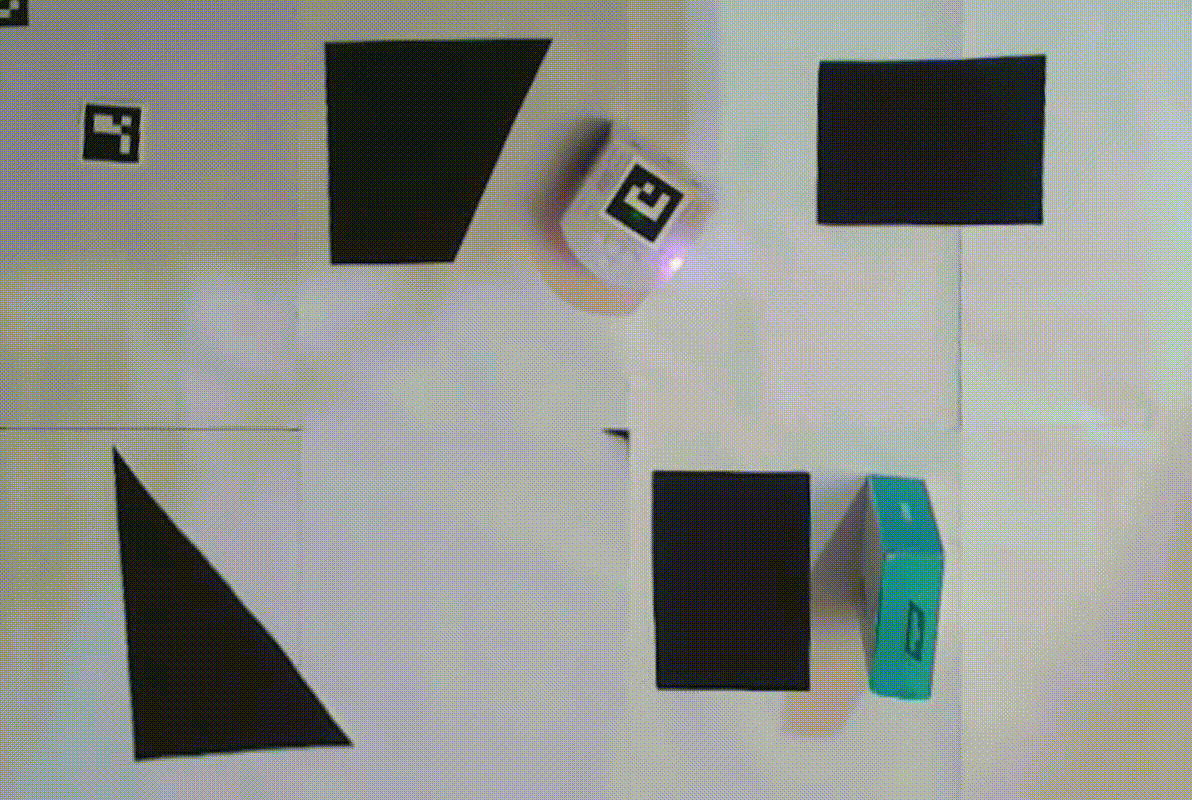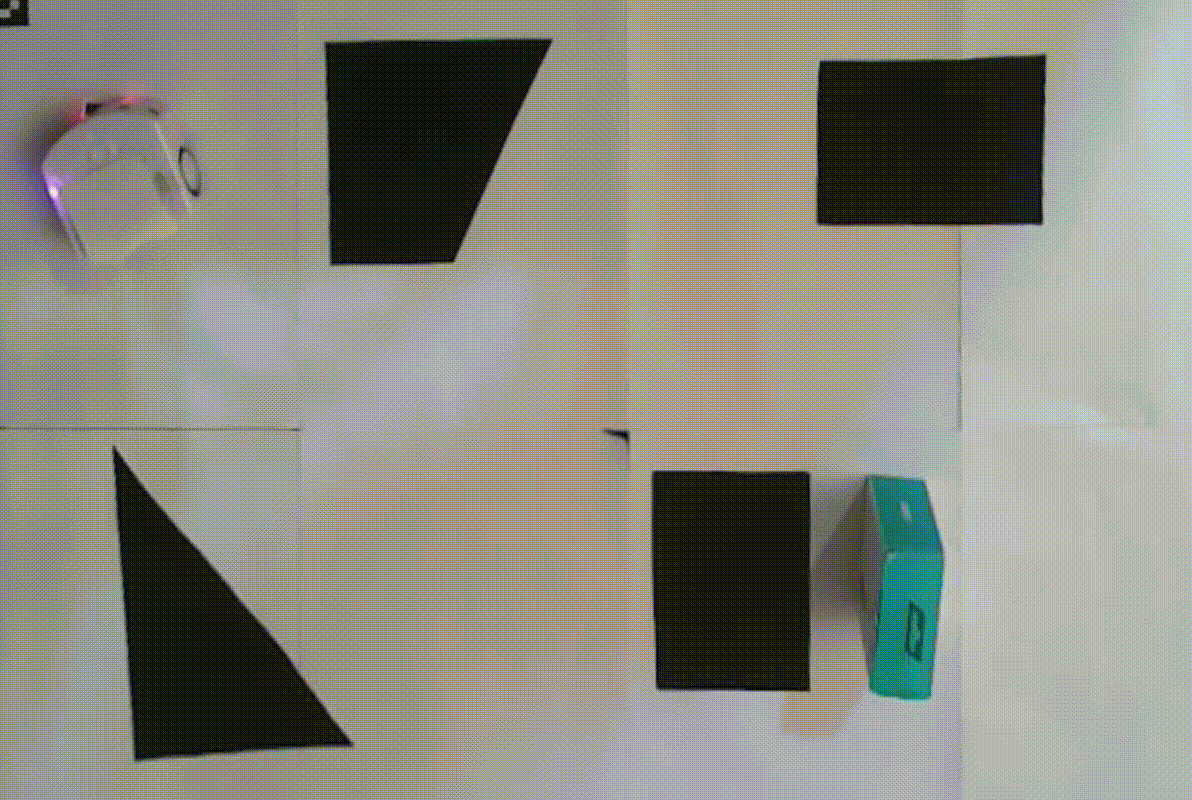
Additional test videos can be found in the ‘videos’ directory of the project repository.
Introduction
The project’s objective is to enable a Thymio robot to navigate a designated environment using a combination of vision-based mapping, global and local navigation strategies, and filtering methods. The environment consists of:
- A white floor bordered by ArUco markers at each corner.
- An ArUco marker placed on the Thymio robot.
- A goal represented by an ArUco marker.
- Static obstacles depicted as black polygons on the map.
- An overhead camera to map static obstacles and compute the optimal path to the goal.
The Thymio robot starts from a random position, with the camera tracking its pose. The robot’s task is to reach the goal by following the optimal path, demonstrating robustness against:
- Dynamic 3D obstacles introduced along its path.
- Temporary occlusions of the camera’s view.
- “Kidnapping” scenarios where the robot is relocated during its operation.
Implementation Features
The system comprises several interconnected modules:
Computer Vision
- Obstacle Detection and Mapping: Utilizes the overhead camera to identify obstacles and construct a map.
- Pose Tracking: Continuously monitors the Thymio’s position and orientation.
Global Navigation
- Path Planning: Computes the optimal path from the robot’s current position to the goal using a visibility graph approach.
Local Navigation
- Waypoint Following: Guides the Thymio along the predetermined path.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Employs proximity sensors to detect and circumvent obstacles in real-time.
Extended Kalman Filter (EKF)
- Pose Estimation: Fuses data from the camera and the robot’s odometry to estimate its pose, ensuring resilience against temporary camera occlusions.
Kidnapping Resilience
- Path Recalculation: Detects significant changes in the robot’s position and recomputes the global path as needed.
Code Structure
The project’s codebase is organized into distinct modules, each responsible for a specific subsystem:
- Computer Vision:
vision_thymio.py - Global Navigation:
global_navigation.py - Extended Kalman Filter:
extended_kalman_filter.py - Local Navigation:
local_navigation.py
Testing scripts for individual subsystems are located in the ‘test’ directory. Additionally, resources related to sensor noise measurement and camera calibration can be found in their respective directories.
Conclusion
This project successfully demonstrates the integration of vision, navigation, and filtering techniques to achieve autonomous navigation of a Thymio robot in a controlled environment. The system exhibits robustness to dynamic obstacles, temporary sensor occlusions, and unexpected relocations, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.